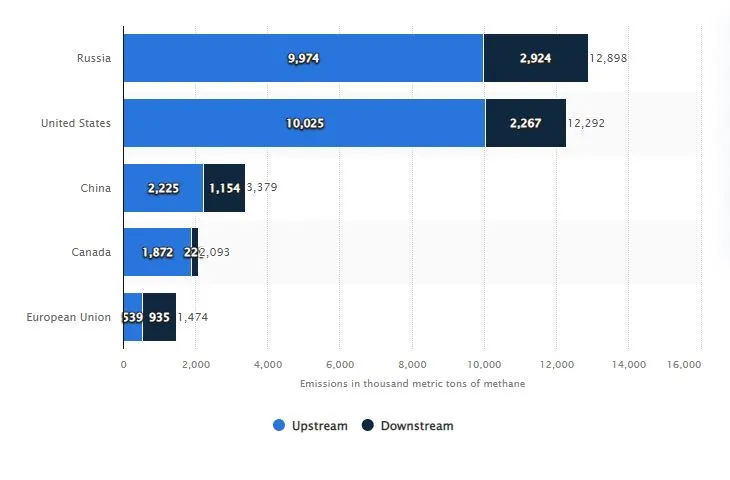
In 2020, Russia emerged as the leading contributor to global methane emissions from oil and gas activities, releasing nearly 13 million metric tons of methane into the atmosphere. The majority of these emissions, approximately 10 million metric tons, were attributed to the upstream sector.
Meanwhile, the United States also reported significant methane emissions, particularly from upstream activities, surpassing those of Russia. However, in contrast to Russia, the downstream sector in the United States witnessed slightly lower methane emissions.
These findings underscore the critical role that different countries play in contributing to methane emissions from the oil and gas value chain. Addressing these emissions is paramount to mitigating climate change and transitioning towards a more sustainable energy future.
Source: Published by N. Sönnichsen (Sep 20, 2021)